PRAGO ANORG
Reliable inorganic products for the most demanding industries
Development of materials for shielding ionizing radiation
We focus on the use of beneficial properties of special metallic materials, polymers, and advanced concretes in the design of inorganic materials for shielding against ionizing radiation, as well as on the practical application of theoretical knowledge in the development of geopolymer materials and the behavior of ionizing radiation particles. Research and testing are carried out in cooperation with ÚACH of the Czech Academy of Sciences, CV Řež, and the Department of Nuclear Reactors at FJFI CTU.
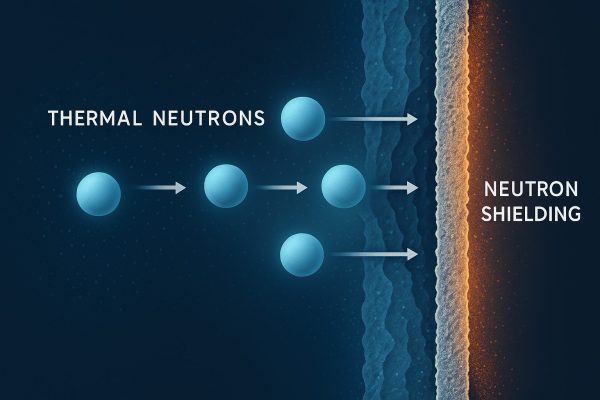
ANORGAN I – one type
A highly efficient inorganic material for shielding thermal neutrons, featuring significantly lower half-value layers than steel, concrete, or polyethylene. Non-flammable, water-resistant, and stable up to 300 °C.
a special inorganic material for shielding thermal neutron flux
significantly lower shielding half-value layers than ballistic steel, concrete and polyethylene
temporarily water-resistant and non-flammable
temperature stability up to 300 °C
bulk density 1.2–1.6 g/cm³
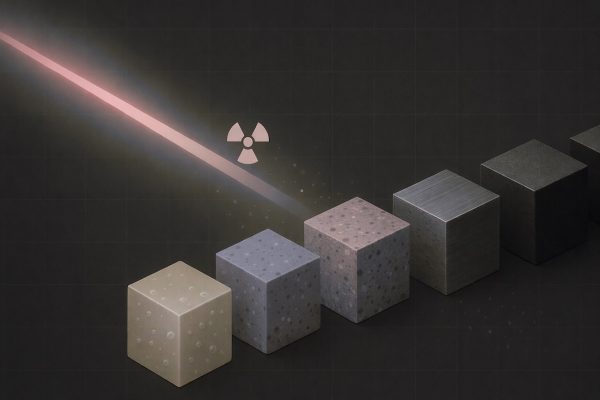
ANORGAN II – 4 types
It offers high efficiency in neutron radiation moderation and absorption, as well as gamma radiation shielding, exceeding common materials such as steel and concrete.
special inorganic materials for shielding a wide spectrum of neutron flux (0–15 MeV)
a set of four material types for moderation and absorption of neutron flux and for gamma-ray shielding, plus a composite material integrating all these functions
significantly lower half-value layers than ballistic steel and concrete; for gamma radiation, markedly higher efficiency than steel, concrete and polyethylene
may be used individually or in combined configurations; the material structure is fully designable
Moderation (H): high hydrogen content (up to 40 mol%), density 1.3–1.5 g/cm³, non-flammable, 100% efficiency up to 250 °C
Absorption (Li): high lithium content (up to 20 mol%), density 1.2–1.3 g/cm³, non-flammable
Gamma shielding (Fe): high iron content (up to 70 mol%), density 2.4–3.8 g/cm³, non-flammable and heat-resistant up to 1000 °C
Composite materials: controlled ratios of effective shielding elements (H, B, Fe), non-flammable, density 1.6–2.0 g/cm³
Technology

pressing of moistened mixtures (pressure up to 10 MPa)

casting of aqueous suspensions into supplied molds

Simple manufacturing and easy handling

easy maintenance and repairability

eco-friendly disposal

non-toxic
Examples of use
Energy
Solutions for nuclear power plants, control centers and key parts of energy infrastructure where reliable, long-term radiation protection of personnel and technology is essential.
Defense
Protection of military facilities, command posts, equipment, logistics bases, and armed forces personnel, including facilities for crisis management and integrated rescue system units.
Health
Shielding for nuclear medicine, diagnostic and therapeutic facilities, sterilization workplaces, and areas for the production and storage of radiopharmaceuticals.
Industry
Safety when working with radiation sources, material inspection, handling of radioactive sources, and applications in geology, water management, archaeology, and forensic science.

Agriculture
Protection of areas used for irradiation, sterilization and pest elimination, with applications in breeding as well as veterinary diagnostics and therapy.
Předběžné experimenty a testování kompozitu

Lid of the container
Lid of the container
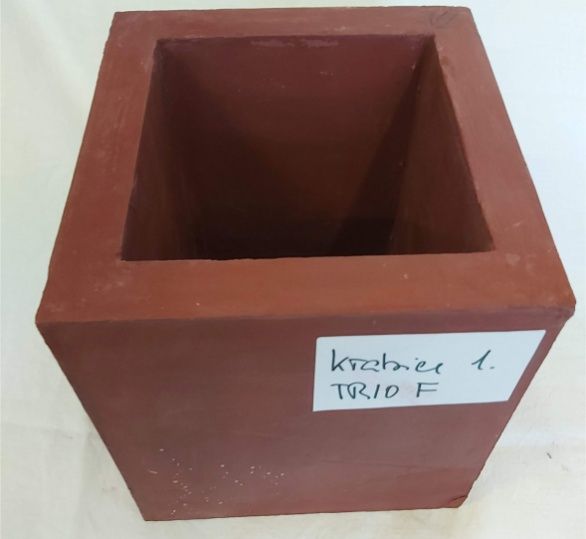

Gamma shielding container
Gamma shielding container
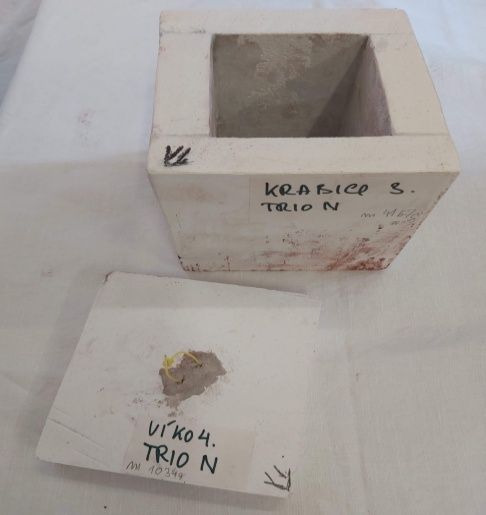

Absorbtion cover
Absorbtion cover
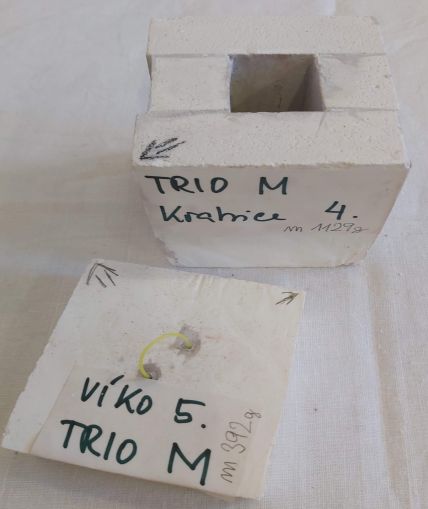

Moderating cover
Moderating cover
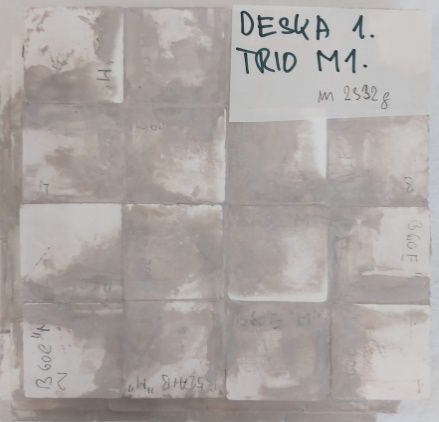

Bonding of the moderating mosaic 1
Bonding of the moderating mosaic 1
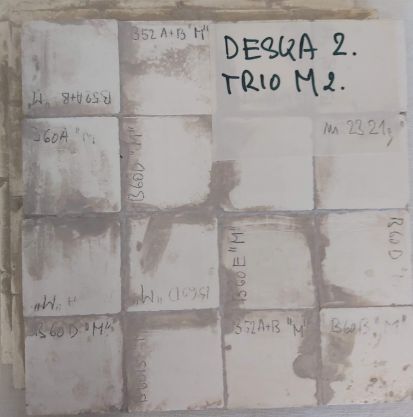

Bonding of the moderating mosaic 2
Bonding of the moderating mosaic 2
